

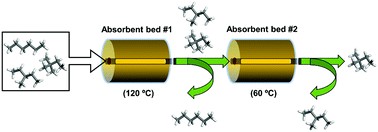
 Separation of alkane isomers represents a crucial process in the petrochemical industry in order to achieve a high octane rating of gasoline. Herein, we report the first example of complete separation of linear, monobranched and dibranched alkane isomers using a single adsorbent. A calcium-based robust microporous metal–organic framework, Ca(H2tcpb) (tcpb = 1,2,4,5-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-benzene), exhibits unique molecular exclusion behavior which enables full separation of binary or ternary mixtures of alkane isomers into the pure form of each isomerate. The successful separation of monobranched and dibranched alkane isomers will not only lead to the production of higher quality gasoline with maximum possible octane numbers but also fill the gap in the current separation technology. Exploration of the separation mechanism indicates that the structural flexibility and adsorbate-dependent structural change of the porous framework play a vital role in the observed temperature-dependent molecular sieving property of the adsorbent.
Separation of alkane isomers represents a crucial process in the petrochemical industry in order to achieve a high octane rating of gasoline. Herein, we report the first example of complete separation of linear, monobranched and dibranched alkane isomers using a single adsorbent. A calcium-based robust microporous metal–organic framework, Ca(H2tcpb) (tcpb = 1,2,4,5-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-benzene), exhibits unique molecular exclusion behavior which enables full separation of binary or ternary mixtures of alkane isomers into the pure form of each isomerate. The successful separation of monobranched and dibranched alkane isomers will not only lead to the production of higher quality gasoline with maximum possible octane numbers but also fill the gap in the current separation technology. Exploration of the separation mechanism indicates that the structural flexibility and adsorbate-dependent structural change of the porous framework play a vital role in the observed temperature-dependent molecular sieving property of the adsorbent.